Symptoms and Diagnosis
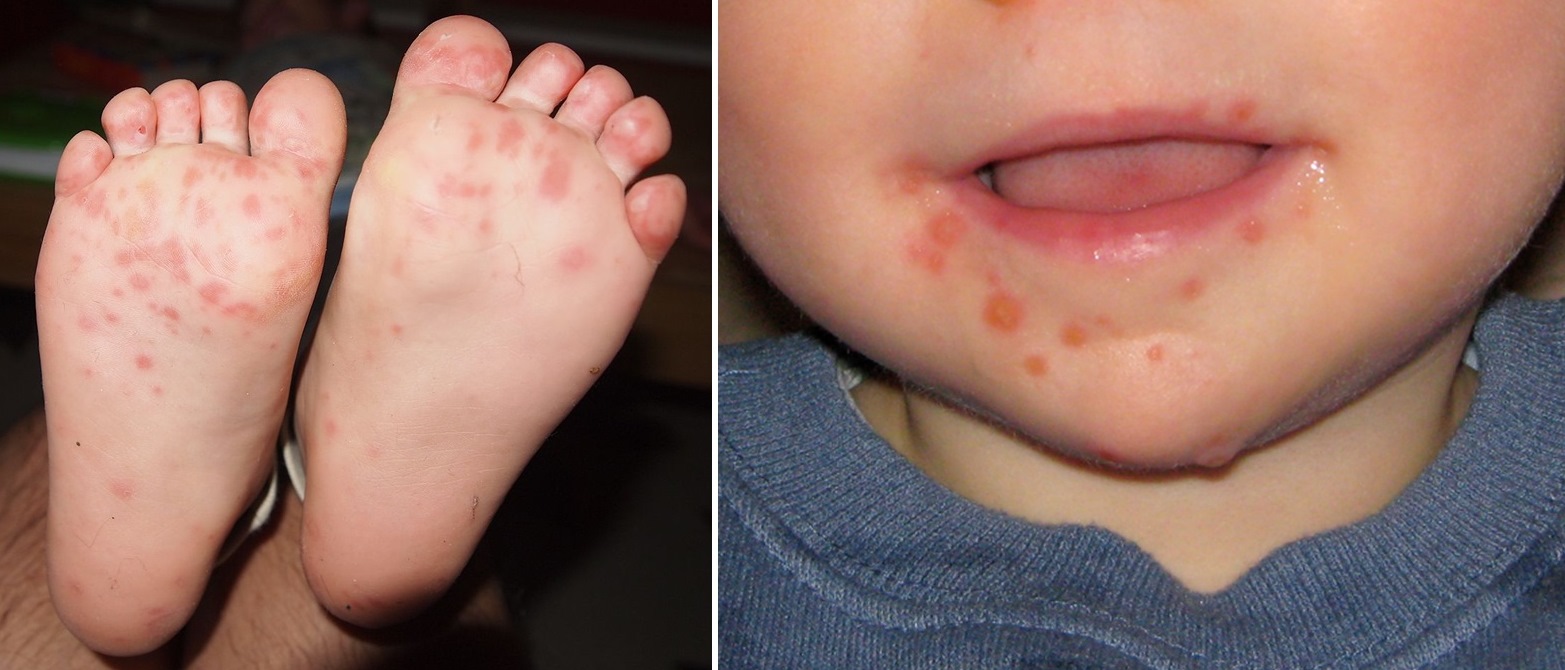
Hand foot and mouth disease – Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood illness caused by a virus. It is characterized by a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth, as well as fever, sore throat, and loss of appetite.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common childhood illness that is caused by a virus. The virus is spread through contact with infected saliva, mucus, or feces. Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease include fever, sore throat, loss of appetite, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth.
The rash can be painful and itchy. There is no specific treatment for hand, foot, and mouth disease, but the symptoms usually go away within a few days. In rare cases, hand, foot, and mouth disease can lead to serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
To prevent the spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease, it is important to wash your hands frequently, avoid contact with infected people, and clean and disinfect surfaces that may have been contaminated with the virus. Mellon Auditorium is a historic concert hall located in Washington, D.C.
The auditorium was built in 1931 and has been the site of many important events, including speeches by presidents and concerts by famous musicians. Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common childhood illness that can be spread through contact with infected saliva, mucus, or feces.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of HFMD are:
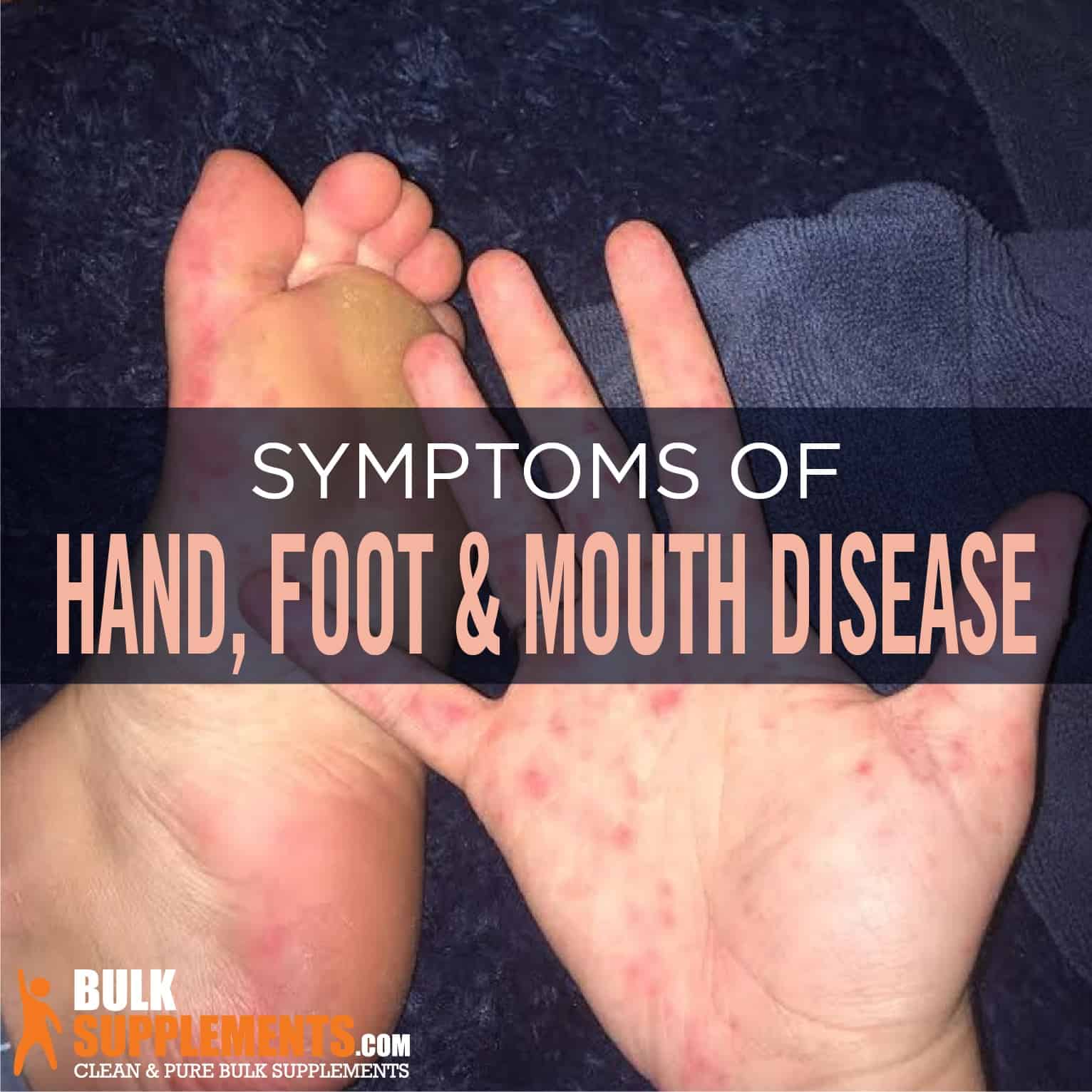
- A rash on the hands, feet, and mouth
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches
Diagnosis
HFMD is diagnosed based on the symptoms and a physical examination. The doctor may also order a blood test to confirm the diagnosis.
Hand foot and mouth disease, a common childhood illness, is caused by a virus. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. While the illness is usually mild, it can be more severe in some cases.
Davante Adams , a wide receiver for the Las Vegas Raiders, recently missed a game due to hand foot and mouth disease. This highlights the fact that the illness can affect anyone, regardless of age or health.
Differential Diagnosis
HFMD can be confused with other childhood illnesses, such as:
- Measles
- Rubella
- Scarlet fever
- Chickenpox
However, HFMD is typically milder than these other illnesses and does not usually cause serious complications.
Treatment and Prevention
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral infection that affects young children. The virus is spread through contact with infected saliva, mucus, or feces. Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease include fever, sore throat, runny nose, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth.
There is no specific treatment for hand, foot, and mouth disease. Treatment is supportive and includes measures to relieve symptoms, such as pain relievers, fever reducers, and mouthwashes. In most cases, hand, foot, and mouth disease resolves on its own within a few weeks.
Preventive Measures, Hand foot and mouth disease
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent the spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease, including:
- Washing hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoiding contact with people who are sick
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that may have been contaminated with the virus
- Staying home from school or work if you are sick
Epidemiology and Transmission: Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infectious disease that primarily affects young children. It is caused by a group of viruses known as enteroviruses, with the most common serotypes being Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus 71. HFMD is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in communities, particularly during the summer and fall months.
Modes of Transmission
HFMD is primarily transmitted through contact with the saliva, mucus, or feces of an infected person. This can occur through direct contact, such as kissing, sharing cups or utensils, or touching contaminated surfaces. The virus can also be spread through airborne droplets produced by coughing or sneezing.
Factors Influencing Transmission
- Age: Children under the age of 5 are most susceptible to HFMD.
- Hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands frequently, can increase the risk of transmission.
- Crowded conditions: Close contact in settings such as daycare centers, schools, and summer camps can facilitate the spread of the virus.
- Time of year: HFMD is most common during the summer and fall months.
- Outbreaks: HFMD can occur in localized outbreaks, particularly in communities with high population density.